|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
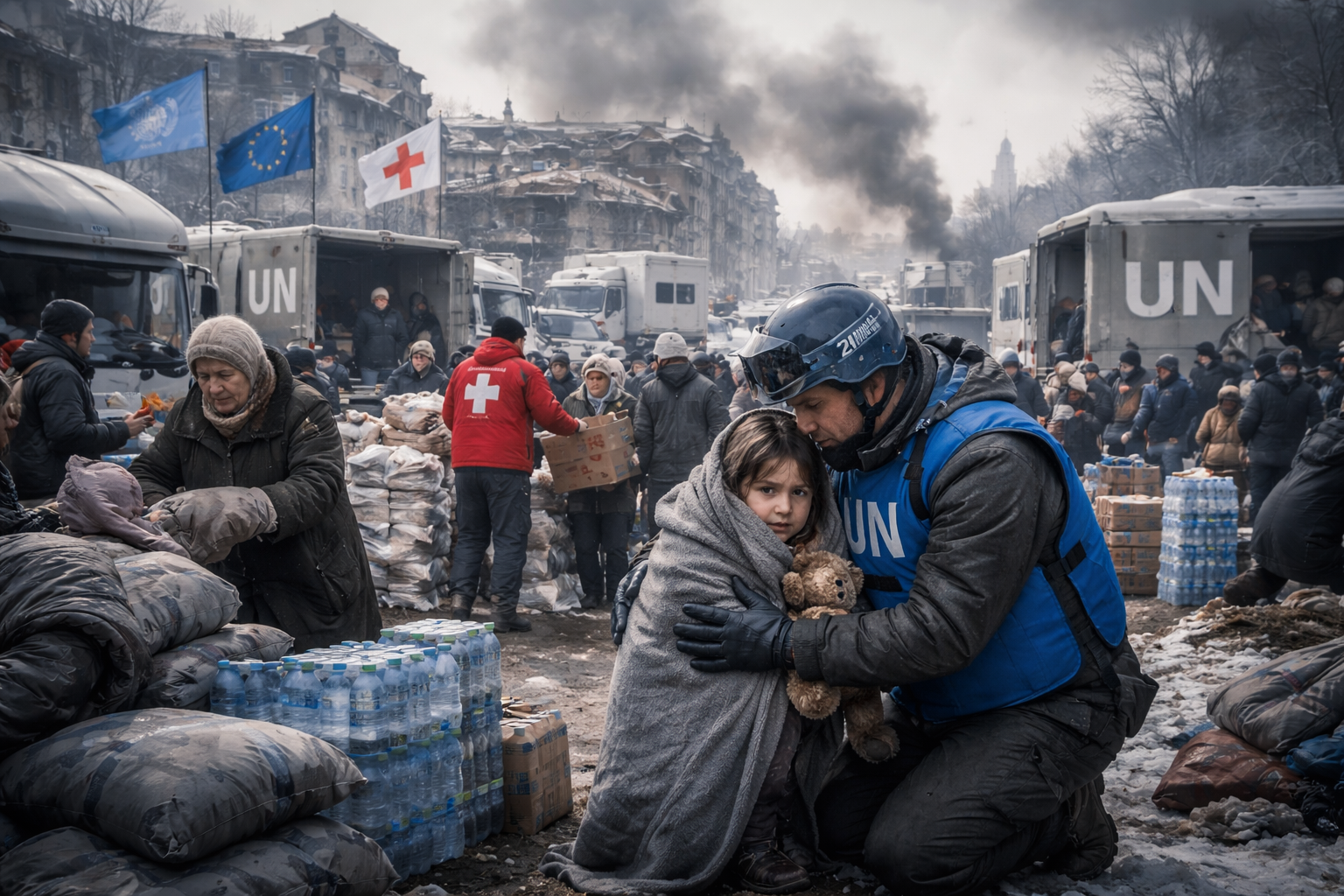
Nearly three years since Russia’s full-scale invasion began, the war in Ukraine continues grinding forward with devastating humanitarian consequences and no clear path to resolution. International aid organizations report that the humanitarian crisis has reached catastrophic levels, with millions of Ukrainians displaced, critical infrastructure destroyed, and winter conditions exacerbating suffering across conflict zones.
The military situation remains stalemated along extensive front lines stretching across eastern and southern Ukraine. Despite significant casualties on both sides, territorial control has shifted minimally in recent months. Ukrainian forces maintain defensive positions while conducting targeted operations, constrained by ammunition shortages and personnel challenges after years of intensive combat. Russian forces continue artillery bombardments and drone attacks targeting both military positions and civilian infrastructure, despite international condemnation of attacks on non-combatants.
Western military assistance to Ukraine faces growing political headwinds. While European nations have generally maintained support commitments, debate intensifies over the sustainability of current aid levels. The United States, traditionally Ukraine’s largest military supporter, is reassessing its assistance under the Trump administration, with signals suggesting potential reductions or conditions attached to future support. Ukrainian officials express deep concern that diminished Western backing could fundamentally alter the strategic balance and force disadvantageous negotiations.
Humanitarian needs have reached unprecedented scales. The United Nations estimates that over 18 million Ukrainians require humanitarian assistance, with 6.3 million internally displaced and approximately 6 million having fled as refugees to other countries. Winter conditions intensify suffering as Russian attacks on energy infrastructure leave millions without reliable electricity, heating, or water. Hospitals operate under extreme duress, lacking essential medicines, equipment, and power for life-saving procedures. Food insecurity affects vulnerable populations, particularly elderly residents unable to evacuate and children suffering malnutrition.
International aid organizations struggle to meet overwhelming needs with insufficient funding. The UN’s humanitarian appeal for Ukraine remains critically underfunded, with donor fatigue evident as the conflict extends beyond initial expectations. Aid workers face significant risks accessing front-line areas, with several humanitarian convoys attacked despite clearly marked vehicles. The International Committee of the Red Cross has documented systematic violations of international humanitarian law by both parties, though Russian forces bear responsibility for the vast majority of civilian targeting.
Reconstruction costs are estimated at over $450 billion a staggering figure that exceeds Ukraine’s pre-war annual GDP multiple times over. Critical infrastructure including power plants, water treatment facilities, transportation networks, schools, and hospitals requires complete rebuilding. The World Bank warns that without substantial international financial commitments, Ukraine’s economic recovery could take decades, creating long-term instability risks for the region.
Diplomatic efforts to end the conflict have stalled. Proposals for peace negotiations face fundamental obstacles, with Russia demanding territorial concessions that Ukraine categorically rejects. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy maintains that negotiations cannot proceed while Russian forces occupy Ukrainian territory, while Russian officials insist on recognizing territorial annexations as preconditions for talks. The absence of trust between parties, combined with dramatically different visions for any settlement, leaves diplomats with little room for progress.
War crimes documentation continues, with investigators collecting evidence of atrocities committed during the conflict. International tribunals are processing cases involving torture, rape, forced deportations, and extrajudicial killings. Thousands of Ukrainian children have been forcibly relocated to Russia a practice that international law characterizes as genocide. Accountability mechanisms face challenges given Russia’s refusal to cooperate with international judicial bodies.
The broader European security architecture remains in flux as the war reshapes continental strategic thinking. NATO has strengthened its eastern flank with additional troops and infrastructure investments. Sweden and Finland’s recent NATO accession reflects the alliance’s expansion in response to Russian aggression. European nations are significantly increasing defense spending, reversing decades of post-Cold War reductions. These developments suggest that regardless of how the Ukraine conflict concludes, European security relationships have fundamentally transformed.
As the war enters another year, Ukrainian resilience continues inspiring international admiration, but the cumulative toll on society, economy, and infrastructure creates immense challenges for the nation’s future. The international community’s sustained engagement will prove critical not only for Ukraine’s immediate survival but for broader principles of sovereignty and international order.