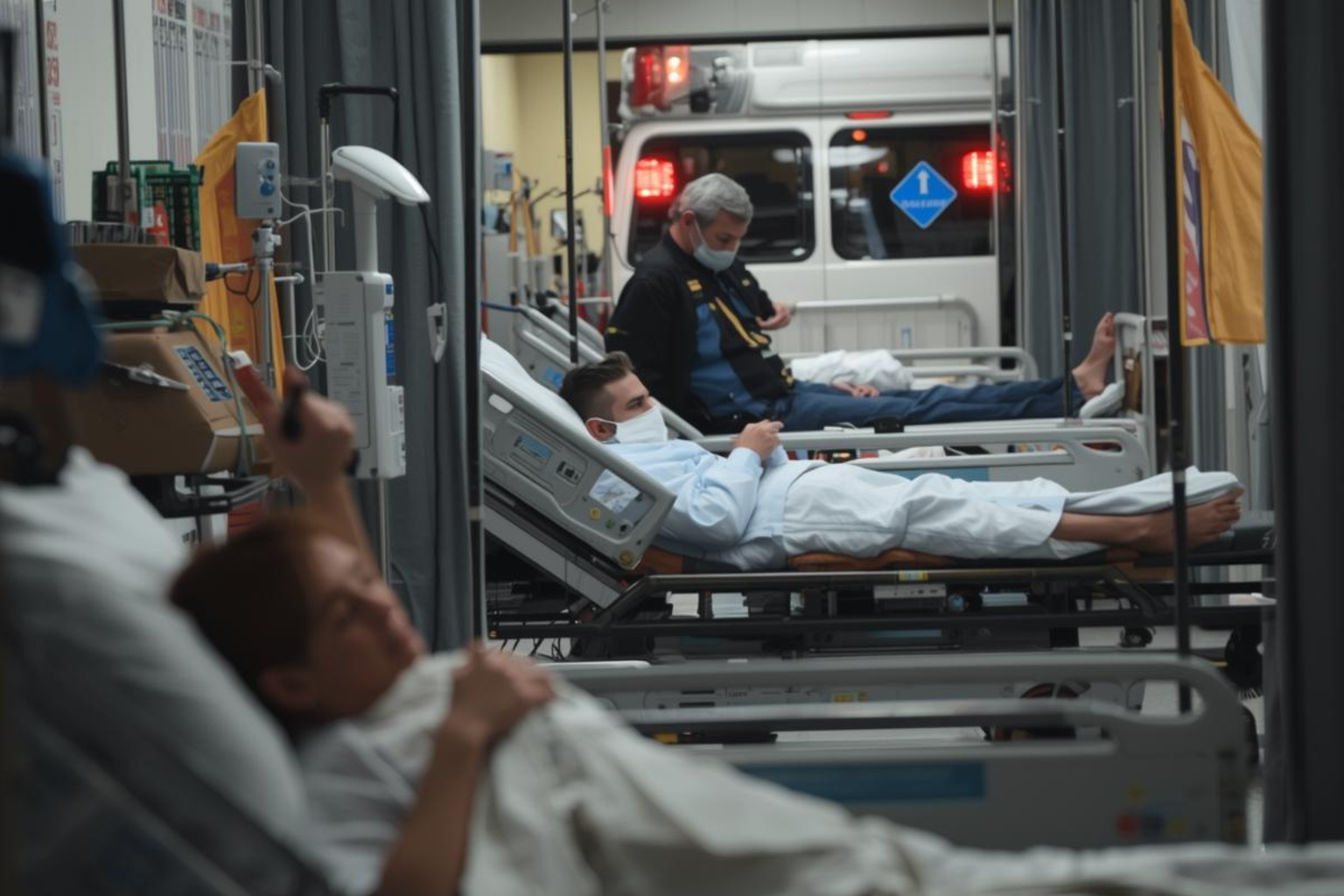
A new H3N2 flu strain is overwhelming hospitals globally, with health officials warning of severe symptoms and questioning vaccine effectiveness as the 2025 flu outbreak intensifies.
Hospitals across the globe are issuing urgent alerts as a powerful new influenza variant pushes healthcare systems to their breaking point. The flu outbreak 2025 has taken medical experts by surprise, with emergency departments from Asia to North America reporting unprecedented patient volumes and admission rates tripling in just three weeks.
The New Flu Strain H3N2: What Makes It Different
The latest H3N2 variant represents a significant genetic shift from previous seasonal influenza strains. Virologists have identified multiple mutations that enhance both transmissibility and the virus’s ability to evade existing immune responses. What sets this strain apart is its capacity to cause serious illness across all age groups, particularly affecting healthy adults aged 30-50 who typically resist severe flu complications.

Global flu cases have surged by an estimated 340% compared to previous years, with countries across Asia, Europe, and North America simultaneously experiencing peak transmission. This synchronized pattern suggests the variant possesses enhanced pandemic potential, prompting the World Health Organization to classify it as a significant public health concern.
Flu Symptoms Severe: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Medical professionals report that flu symptoms severe in nature are becoming increasingly common with this variant. Unlike typical seasonal influenza, patients are experiencing more intense and prolonged illness that requires immediate medical attention.
Key symptoms include:
- Severe respiratory issues: Persistent coughing lasting weeks, shortness of breath, and chest pain affecting approximately 40% of hospitalized cases
- High-grade fevers: Temperatures exceeding 103°F lasting more than five days, accompanied by debilitating body aches
- Neurological complications: Severe headaches, confusion, and in rare cases, brain inflammation
- Gastrointestinal distress: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea appearing in nearly 30% of cases
Healthcare experts urge individuals experiencing difficulty breathing, persistent chest pain, sudden dizziness, confusion, or inability to keep fluids down to seek immediate emergency care. These warning signs may indicate dangerous complications requiring urgent intervention.
Flu Vaccine Effectiveness: A Critical Concern
Perhaps the most troubling aspect involves questions about flu vaccine effectiveness against the new variant. Preliminary data suggests current seasonal flu vaccines offer reduced protection, with effectiveness estimates ranging from 30-45% significantly lower than the typical 50-60% effectiveness rate.
This reduced efficacy stems from antigenic drift, the genetic changes that allow flu viruses to partially evade immune responses. However, immunologists emphasize vaccination still provides meaningful benefits. Vaccinated individuals who contract the virus generally experience milder symptoms, shorter illness duration, and significantly lower hospitalization rates compared to unvaccinated individuals.
Healthcare authorities are exploring accelerated development of updated vaccine formulations while increasing production of antiviral medications to combat the outbreak.
Regional Impact and Healthcare Strain
The Asia-Pacific region reported the earliest cases, with Japan, South Korea, and Singapore seeing hospital admissions triple within weeks. European nations including France, Germany, and the United Kingdom are operating above normal capacity, with some hospitals converting outpatient areas into temporary flu wards.
North America faces simultaneous outbreaks across multiple regions, with emergency departments reporting 60-80% of respiratory illness visits are flu-related. Even the Southern Hemisphere, typically in its low flu season, is experiencing continued transmission suggesting this virus may not follow traditional seasonal patterns.
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Antiviral medications like oseltamivir remain the frontline treatment when administered within 48 hours of symptom onset. However, supply constraints in some regions have necessitated careful prioritization for high-risk patients.
Effective prevention methods include:
- Frequent handwashing with soap for at least 20 seconds
- Covering coughs and sneezes, and wearing masks in crowded indoor settings
- Maintaining physical distance and staying home when ill
- Improving indoor ventilation and disinfecting high-touch surfaces
- Getting vaccinated despite reduced effectiveness
The Path Forward
Epidemiological models suggest the outbreak may peak within four to eight weeks in currently affected regions, though flu viruses remain inherently unpredictable. The scientific community is leveraging real-time genomic sequencing, AI algorithms for transmission prediction, and rapid vaccine development platforms that could produce updated formulations within months.
While the situation is serious and healthcare systems face legitimate strain, the vast majority of flu cases resolve with proper care and time. By combining individual responsibility with community solidarity and following evidence-based guidance from health authorities, we can navigate this outbreak while minimizing its impact on public health and daily life. Staying informed through reliable sources and taking reasonable precautions will prove essential to overcoming this global health challenge.